The PEG Ratio - A Growth-Oriented Approach to Stock Valuation
Introduction:
In the bustling marketplace of stocks, understanding the true value of a company requires more than just looking at the P/E ratio. Enter the PEG ratio, a metric that brings growth into the valuation equation, offering a clearer picture of whether a stock is priced appropriately for its potential.

What is the PEG Ratio?
The PEG ratio is calculated by dividing the P/E ratio by the company’s expected earnings growth rate:

Why Use PEG Over P/E?
– Growth in Context: While P/E gives you a snapshot of current valuation, PEG considers future growth, making it invaluable for growth investing.
– Value or Overvalue: A PEG below 1 might indicate an undervalued stock relative to its growth, while above 1 could suggest overvaluation unless justified by exceptional growth prospects.
Example:
Imagine Company A has a P/E ratio of 30 and an expected annual EPS growth rate of 15%. The PEG ratio would be:
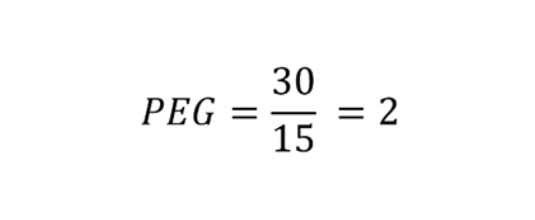
This suggests that the stock might be overvalued for its growth rate, unless there are other factors at play like market dominance or technological breakthroughs.
Application in Stock Selection:
– Comparative Analysis: Use PEG to compare companies within the same sector, seeking those with lower ratios for potentially better investment opportunities.
– Long-term Perspective: PEG encourages investors to think about future earnings, aligning investments with long-term growth stories.
Conclusion:
The PEG ratio is a powerful tool for investors looking to marry value with growth. It helps in identifying stocks where the market might not fully appreciate the growth potential, offering opportunities to buy into future success at today’s prices.