Is Your Stock in the ICU? Do a Quick Checkup with the ICR
Introduction:
Debt is a double-edged sword in corporate finance; it can fuel growth or lead to downfall. The Interest Coverage Ratio (ICR) offers investors a lens to assess how well a company can manage its debt, focusing on its ability to cover interest expenses from operational earnings.

What is the Interest Coverage Ratio?
The ICR is calculated by dividing Earnings Before Interest and Taxes (EBIT) by the interest expense:
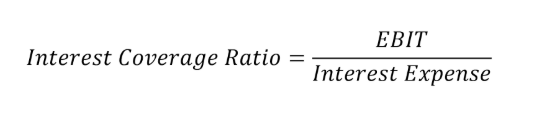
Why It's Crucial:
– Financial Health Indicator: It reveals how many times a company can pay its interest obligations with its current earnings, highlighting financial resilience or vulnerability.
– Risk Assessment: Beyond raw debt figures, ICR provides insight into how debt might strain a company’s operations, especially in volatile economic conditions.
Example:
Consider Company B with an EBIT of Rs. 5,00,00,000 and annual interest expenses of Rs. 1,00,00,000. The Interest Coverage Ratio would be:
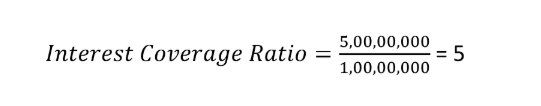
This ratio of 5 means Company B earns enough to cover its interest expense five times over, suggesting a strong ability to manage its debt obligations.
Application in Investment Decisions:
– Stability Over Time: Look for trends in ICR to gauge if a company is improving its financial health or if it’s becoming more leveraged.
– Sector-Specific Norms: Understand that acceptable ICR levels can vary by industry; sectors with stable cash flows might operate with lower ratios without undue risk.
Conclusion:
The Interest Coverage Ratio is an essential tool for investors concerned with a company’s debt sustainability. It helps in distinguishing between companies that leverage debt wisely for growth and those that might be on the brink of financial distress. By integrating ICR into your analysis, you’re better positioned to select stocks that not only grow but also maintain robust financial health.
